VISUALIZING THE SCALE OF OUR PLANETARY NEIGHBORHOOD.

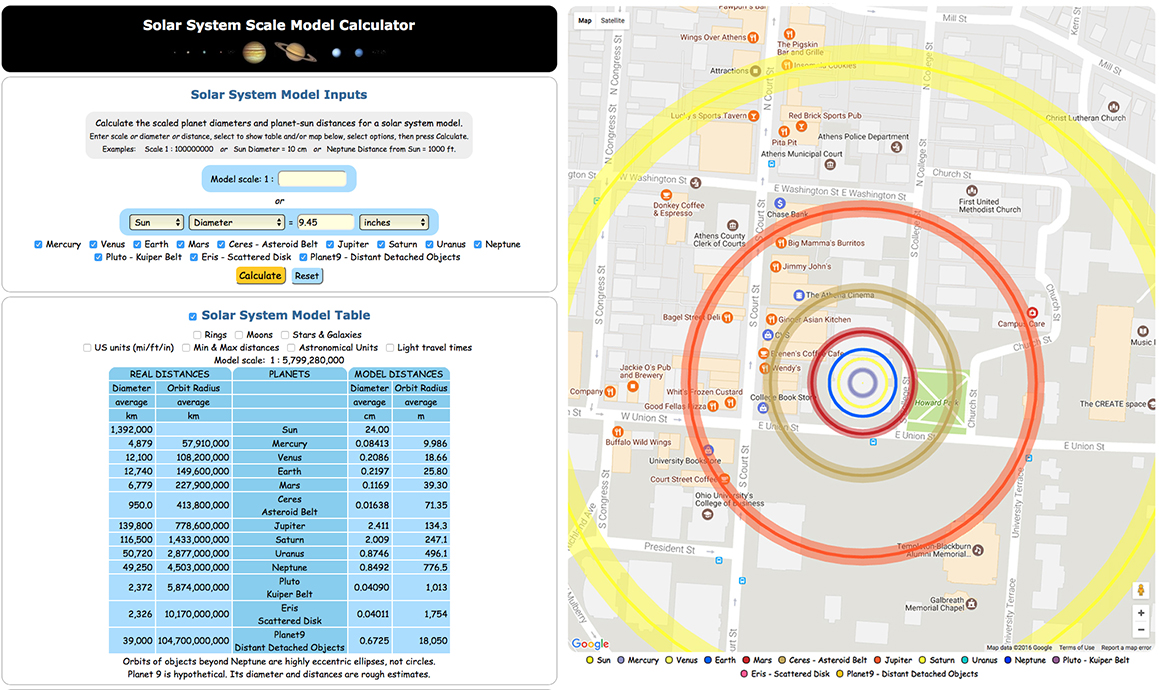
When I glue a basketball to the top of a pole in my garden, and tell people that it’s the sun, they will probably suggest that I seek urgent medical care. They are unlikely to know that it’s the first stage of my local solar model, and that I soon will be gluing a tiny .09 inch (0.22 cm) blue sphere, representing the Earth, to a fence 85 feet (25.8 meters) away. Using an online calculator, it’s easy to input any size of Sun at any location, and get the corresponding scale model metrics. This is the essential first stage in planning the big diagram. http://thinkzone.wlonk.com/SS/SolarSystemModel.php
The Sun in proportion to the planets.

There are representations of the solar system, at various sizes, in many locations. Here are a few examples.
SWEDISH MEGA-SIZE
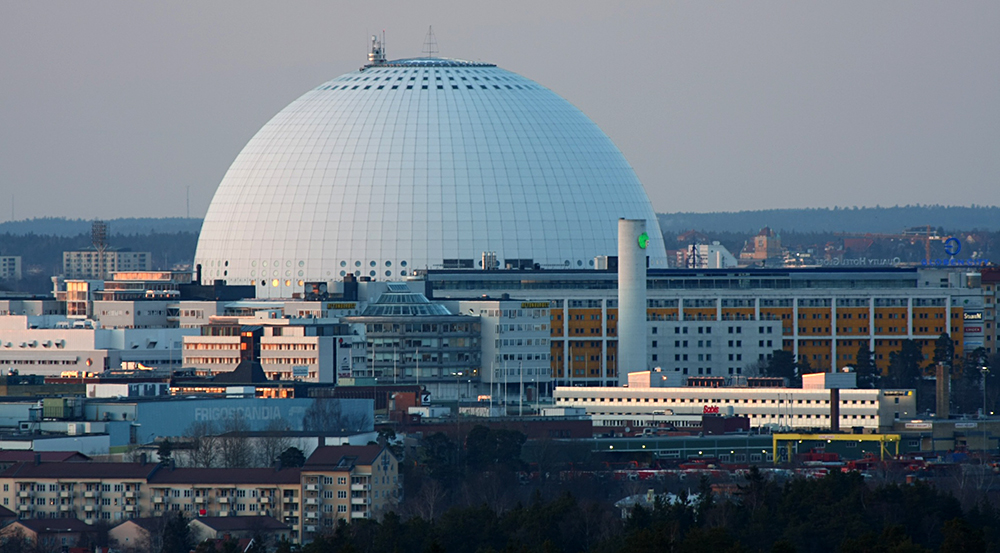

(Photograph: bengt-re)
The world’s largest solar model is in Sweden. The Sun is represented by the huge Ericsson Globe in Stockholm. The indoor arena has a diameter of 361 feet (110 meters). Sedna, a large minor planet, is 4 inches (10 cm) in diameter, and 567 miles (912 km) from the globe, way up in the north of the country. This would be out in the farthest reaches of the solar system. http://www.swedensolarsystem.se/en/

(Photograph: Dag Lindgren)
MAINE MID-SIZE

(Photograph: Michael York/The Maine Solar Model)
The Maine Solar System Model covers 95 miles (153 km). http://pages.umpi.edu/nmms/solar/
The Sun is sometimes a painted ring, sometimes a painted shape, on multiple floors inside the University of Maine, and is 49.5 feet (15 meters) in diameter. The 5.5 inch (14 cm) fiberglass Earth is outside a car sales location just 1 mile (1.6 km) away. It’s another 39 miles (63 km) down the road past models of all the planets to 1 inch (2.54 cm) Pluto (still a planet in those days, and despite being since downgraded, is after all, still orbiting the Sun). They’ve added a dwarf planet, Eris, discovered in 2005, which is a stunning 54.5 miles south of Pluto at this scale. It’s one of the farthest known objects in the Solar System.
SAGAN COMPACT

(Photographs: Teresacurl)
The much smaller Carl Sagan Planet walk was built in 1997 in Ithaca, New York, in memory of it’s very influential resident. It’s 0.7 miles (1.18 km) from the 10.9 in. (27.8 cm) diameter Sun to tiny Pluto, which is 0.2 inches in diameter (0.05 cm). The Sun-sized opening is a constant to compare the planets against.
http://www.sciencenter.org/sagan-walk.html
DESERT ORBITS
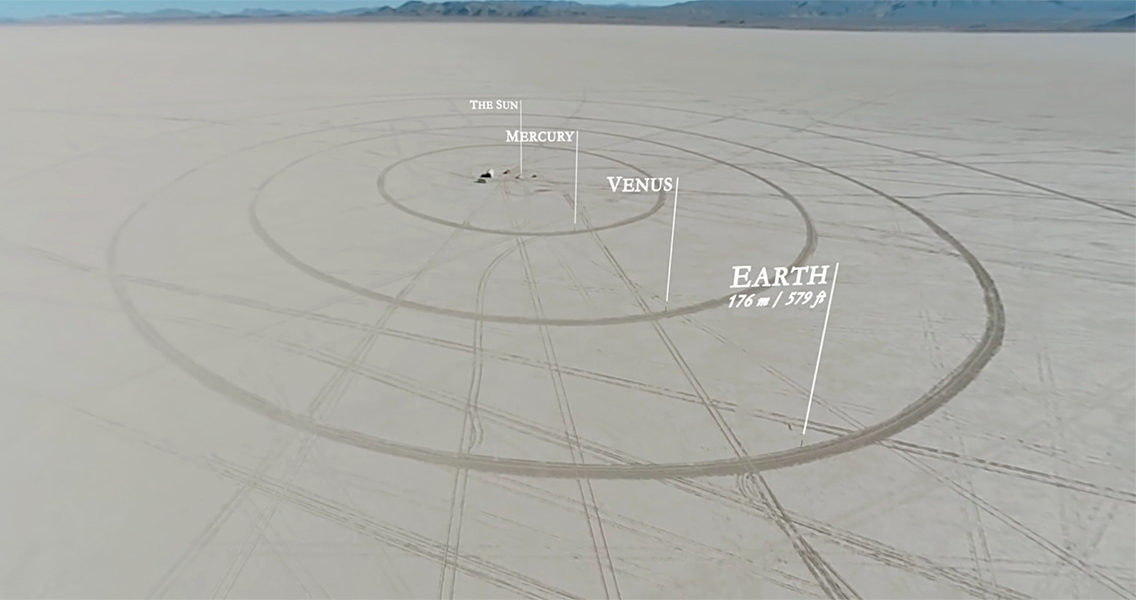
A creative solar model constructed in a Nevada lakebed. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zR3Igc3Rhfg
GOING MOBILE
Rotating planets by Authentic Models. (Available from numerous online retailers.) Clearly not to scale. So if you give this a gift, make sure the recipient knows not to use it for calculating space probe trajectories.